当前位置:首页 > 考研频道 > 考研真题 > 1982年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题
发布时间:2021-03-19 关键词:研究生入学统一考试,英语试题
摘要:多练以前的真题,才能了解自己的水平。给大家整理了1982年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题+答案。
1982年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题
Section I Structure and Vocabulary
In each question, decide which of the four choices given will complete the sentence if inserted at the place marked. Circle the letter before your choice. Only one choice is to be circled (12 points)
EXAMPLE:
(1) The matter ________ you were arguing about last night has been settled.
[A] what
[B] as
[C] whom
[D] that
ANSWER: [D]
(2) We must not rule ________ the possibility of miscalculation.
[A] away
[B] off
[C] out
[D] up
ANSWER: [C]
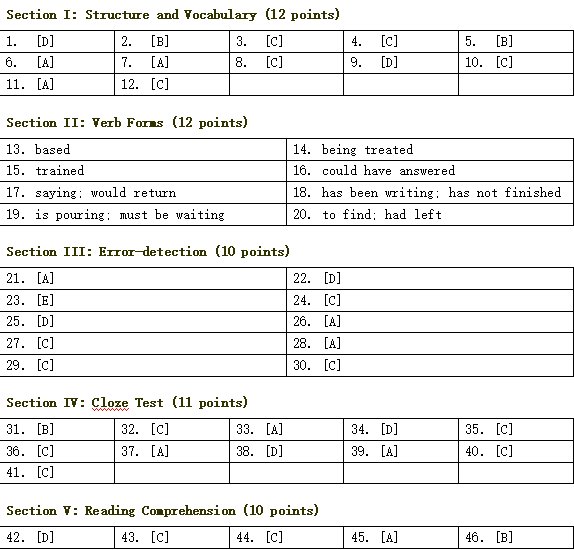
1. You never told us why you were late for the last meeting, ________?
[A] weren’t you
[B] didn’t you
[C] had you
[D] did you
2. I have to get ________ about the subject before I write the paper.
[A] a few more informations
[B] a little more information
[C] a few more information
[D] a little more informations
3. Only when you have acquired a good knowledge of grammar ________ write correctly.
[A] you will
[B] you can
[C] can you
[D] can’t you
4. ________ it is you’ve found, you must give it back to the person it belongs to.
[A] That
[B] Because
[C] Whatever
[D] However
5. Although ________ happened in that developed country sounds like science fiction, it could occur elsewhere in the world.
[A] which
[B] what
[C] how
[D] it
6. He studied hard at school when he was young ________ contributes to his success in later life.
[A] , which
[B] therefore
[C] which
[D] so that
7. He felt it rather difficult to take a stand ________ the opinion of the majority.
[A] against
[B] by
[C] to
[D] in
8. I need a book dealing ________ anti-pollution problems.
[A] about
[B] on
[C] with
[D] to
9. He has been asked to account ________ his absence.
[A] of
[B] on
[C] about
[D] for
10. Science has brought ________ many changes in our lives.
[A] out
[B] into
[C] about
[D] forward
11. How did it come ________ that you made a lot of mistakes in your homework?
[A] about
[B] after
[C] with
[D] to
12. Science has brought ________ many changes in our lives.
[A] for
[B] to
[C] in
[D] with
Section II Verb Forms
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate forms of verbs given in brackets. (12 points)
EXAMPLE:
(1) Will you call them up and tell them we'll start as soon as the rain ________ (stop)?
ANSWER: stops
(2) ________ (See) from the moon, our Earth looks like a big bright disk.
ANSWER: Seen
13. The author gave a detailed description ________ (base) on his personal observation of nature.(were defeated/had been defeated)
14. The way he talks is simply intolerable I object to ________ (treat) like a child.(were defeated/had been defeated)
15. These students are quick at learning. We’ll have them ________ (train) in new methods.(were defeated/had been defeated)
16. Had she been given some information, she ________ (can answer) the questions.(were defeated/had been defeated)
17. Helen borrowed my dictionary the other day ________ (say) that she ________ (return) it soon.(were defeated/had been defeated)
18. Mary always has a lot of letters to write. She ________ (write) letters all afternoon and she still ________ (not finish).(were defeated/had been defeated)
19. We promised them to be there by 5 o’clock. Now it’s 4:50 already, and the rain ________ (pour) down like this. They ________ (must wait) for us impatiently.(were defeated/had been defeated)
20. Mr. Green ran all the way up to the station only ________ (find) that the train ________ (leave) fifteen minutes before.(were defeated/had been defeated)
Section III Error-detection
Each question consists of a sentence with four underlined parts (words or phrases). These parts are labeled [A], [B], [C], and [D]. Choose the part of the sentence that is incorrect, and circle the letter of your choice. If you find no mistakes in a sentence, circle the letter E for "No Error". Only one choice is to be circled. (10 points)
EXAMPLE:
1) The plant manager, likeA many workers, wereB very experiencedC inD safety precautions. No ErrorE
ANSWER: [B]
2) To comprehend wellA, aB student mustC read frequentlyD. No ErrorE
ANSWER: [E]
21. If the policeman would haveA arrivedB earlier, he would haveC seenD the accident. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
22. The tasksA of the directorB are greater thanC his assistantD. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
23. NeitherA the teacher norB the students wereC introduced to theirD dean. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
24. The visibility became so badA thatB I could not hardlyC see the man who was walking one footD in front of me. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
25. She hungA upB all the clothes that has beenC layingD around the room. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
26. The amountA of hours we spent onB the work was ratherC smallD. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
27. The lecturer is a person withA great promiseB and whoC should beD encouraged. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
28. My name is William, andA most ofB my friends callC me Bill for shortD. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
29. We stronglyA suggest thatB Smith is toldC about hisD physical condition as soon as possible. No ErrorE([C] approve of)
30. The group isA waitingB for theirC plane toD Beijing. No ErrorE([C] approve of)(were defeated/had been defeated)
Section IV Cloze Test
For each numbered blank in the following passage there are four choices labeled A, B, C, and D. Choose the correct one and circle the letter before your choice. Only one choice is to be circled. (11 points)
EXAMPLE:
____1____ the final scene I noticed him ____2____ his eyes..
1. [A] During
[B] While
[C] As soon as
[D] No sooner than
2. [A] to wipe
[B] wiping
[C] to be wiped
[D] having wiped
ANSWER: 1. [A] 2. [B]
before man learned how to build houses, he natural shelters, as the animals did. He found that he could himself by climbing up into trees or by crouching the overhanging edges of cliffs, or by crawling into . The first shelters or homes actually built by man were very simple. For his building , he used what he could find easily him: rocks, tree branches, dried grasses, animal skins. It was , however, before man began to build shelters because man learned to farm, he lived by .
31. [A] Epoch
[B] Long
[C] Time(A)
[D] Age
32. [A] looked after
[B] looked about
[C] looked for(D)
[D] looked into
33. [A] protect
[B] confine
[C] bury(B)
[D] cover
34. [A] to
[B] above
[C] into(C)
[D] under
35. [A] cracks
[B] pits
[C] caves(B)
[D] cavities
36. [A] rocks
[B] substance
[C] materials(D)
[D] groundwork
37. [A] around
[B] above
[C] under(B)
[D] over
38. [A] in time
[B] many a time
[C] behind the time(A)
[D] a long time
39. [A] permanent
[B] unchangeable
[C] changeable(A)
[D] perpetual
40. [A] if
[B] in case
[C] until(C)
[D] after
41. [A] fishing
[B] gaming
[C] hunting(C)
[D] shooting
Section V Reading Comprehension
Each sentence or paragraph below is followed by four statements. One of the statements is a suggestion which can be drawn from the information given in the original sentence or paragraph. Read the sentences and paragraph carefully and circle your choice. Only one choice is to be circled. (10 points)
EXAMPLE:
Whether the study of the lunar rocks will answer the long debated question of the origin of the moon remains to be seen.
[A] The speaker wants to remain behind to see whether the study will throw light on the question.
[B] The speaker feels that the study will probably answer the question.
[C] The speaker is sure that the study will produce an answer to the question.
[D] The speaker is not sure whether the study will answer the question or not.
ANSWER: [D]
42. If this book begins with a familiar them — the Indian experience of the last 120 years — the author brings to it great power and deep understanding.
[A] This means that the book was written 120 years ago.
[B] This means that the Indian experience of the last 120 years is a familiar experience, and nothing new can be written about it.
[C] This means that the book lacks understanding of the Indian experience.
[D] This means that the writer of this sentence likes the book.
43. I disagreed then as now with many of John Smith’s judgments, but always respected him, and this book is a welcome reminder of his big, honest, friendly, stubborn personality.
[A] The writer of this sentence dislikes John Smith, but agrees with his ideas.
[B] The writer of this sentence considers John Smith to be a disagreeable person.
[C] The writer of this sentence disagrees with John Smith but respects him.
[D] The writer of this sentence disagreed with him then but agrees with him now.
44. Just before his tenth birthday John received a horse from his father; this was the first of a series of expensive gifts intended to create the impression of a loving parent.
[A] John received the horse because he was ten.
[B] John received the horse because his father loved him.
[C] John received the horse because his father wanted to seem loving.
[D] John received the horse because his father wouldn’t be able to give him expensive gifts in the future.
45. It cannot be doubted that without intelligence and diligence on the part of the students themselves, as indeed without the leadership and the coaching of the teachers, a good examination result will not come.
[A] This sentence means that for a good result of an examination both the intelligence and diligence of the students and the guidance of the teachers must be stressed.
[B] This sentence means that a good result of examination will come without either the students’ effort or that of the teachers.
[C] This sentence means that a good examination result depends chiefly on the correct guidance of the teachers.
[D] This sentence means that a good examination result depends on either the students or the teachers.
46. Industry and commerce are the largest users of electrical energy. Using less electricity would mean a reduced industrial capacity and fewer jobs in the affected industries. Therefore an unfavorable change in our economic structure might result.
[A] This means that decreasing the use of electricity must begin immediately.
[B] This means that decreasing the use of electricity will cause difficulties.
[C] This means that decreasing the use of electricity isn’t important.
[D] This means that decreasing the use of electricity won’t affect industry.
Section VI Chinese-English Translation
Translate the following sentences into English. (15 points)
47. 随着时间的过去,他将会懂得我所讲的话。
48. 听说那个地区的工厂比1970年增加了两倍。
49. 在这个季节保持蔬菜新鲜可不容易。
50. 只要我们继续努力工作,我们就能提前完成任务。
51. 尽管我们的政治和经济制度存在着巨大差异,我们两国在许多方面有着共同的利益。
Section VII English-Chinese Translation
Choose either of the following two passages and translate it into Chinese. (30 points)
(1)
In country after country, talk of non-smokers’ right is in the air. While a majority of countries have taken little or no action yet, some 30 nations have introduced legislative steps to control smoking. Many laws have been introduced in other countries to help clear the air for nonsmokers, or to cut cigarette consumption.
In some developed countries the consumption of cigarettes has become more or less stabilized. However, in many developing nations, cigarette smoking is seen as a sign of economic progress — and is even encouraged. As more tobacco companies go international, new markets are sought to gain new smokers in those countries. For example, great efforts are made by the American tobacco industry to sell cigarettes in the Middle East and North Africa — where U.S. tobacco exports increased by more than 27 percent in 1974.
Smoking is harmful to the health of people. World governments should conduct serious campaigns against it. Restrictions on cigarette advertisements, plus health warnings on packages and bans on public smoking in certain places such as theatres, cinemas and restaurants, are the most popular tools used by nations in support of nonsmokers or in curbing smoking. But world attention also is focusing on another step which will make the smoker increasingly self-conscious and uncomfortable about his habit. Great efforts should be made to inform young people especially of the dreadful consequences of taking up the habit. And cigarette price should be boosted.
In the long run, there is no doubt that everybody would be much better-off if smoking were banned altogether, but people are not ready for such drastic action.
(2)
Nuclear power’s danger to health, safety, and even life itself can be summed up in one word: radiation.
Nuclear radiation has a certain mystery about it, partly because it cannot be detected by human senses. It can’t be seen or heard, or touched or tasted, even though it may be all around us. There are other things like that. For example, radio waves are all around us but we can’t detect them, sense them, without a radio receiver. Similarly, we can’t sense radioactivity without a radiation detector. But unlike common radio waves, nuclear radiation is not harmless to human beings and other living things.
At very high levels, radiation can kill an animal or human being outright by killing masses of cells in vital organs. But even the lowest levels can do serious damage. There is no level of radiation that is completely safe. If the radiation does not hit anything important, the damage many not be significant. This is the case when only a few cells are hit, and if they are killed outright. Your body will replace the dead cells with healthy ones. But if the few cells are only damaged, and if they reproduce themselves, you may be in a deformed way. They can grow into cancer. Sometimes this does not show up for many years.
This is another reason for some of the mystery about nuclear radiation. Serious damage can be done without the victim being aware at the time that damage has occurred. A person can be irradiated and feel fine, then die of cancer five, ten, or twenty years later as a result. Or a child can be born weak or liable to serious illness as a result of radiation absorbed by its grandparents.
Radiation can hurt us. We must know the truth.
1982年考研英语真题答案